InflammaSkin® human psoriasis model
The only T cell driven psoriasis skin model
The InflammaSkin® psoriasis model
A unique platform to study anti-psoriasis drugs

Today’s preclinical skin models may closely mimic the inflammatory features of psoriasis, but they often lack tissue complexity and immune cell diversity. Moreover, they generally don’t allow testing the subcutaneous delivery of therapeutic compounds. The InflammaSkin® human psoriasis model is a unique, T-cell driven skin inflammation model that allows to efficiently study the response of real human skin to anti-psoriasis drugs and compounds after topical or subcutaneous administration. Below you’ll find a quick overview of the model’s features and benefits.
Standardized
InflammaSkin® models are standardized human skin models that allow for reproducible research and testing on anti-psoriasis drugs.
Immunocompetent
The models are alive, functional and immunocompetent. They contain all structural and immunological cell types and appendages for relevant data.
T-cell activated
InflammaSkin® models are currently the only ex vivo psoriasis skin model on the market with a T-cell driven inflammation featuring the Th1/Th17 phenotype.
Platform
InflammaSkin® models are suitable for prophylactic and therapeutic biologics as well as small molecule drugs, which require topical or subcutaneous administration.
Live response from real human skin
A full week of testing opportunities
The InflammaSkin® model is composed of real human skin that is kept alive using a nourishing gel matrix. Its technology is based on our patented NativeSkin® platform, which allows us to keep donated human skin alive for 7 days after surgery and give our customers a week-long window of testing opportunities. The InflammaSkin® model always contains real human epidermis and dermis and may also contain the associated adipose tissue to allow for subcutaneous injection, depending on your needs.
The only T cell driven human psoriasis model
Unique technology for reliable data

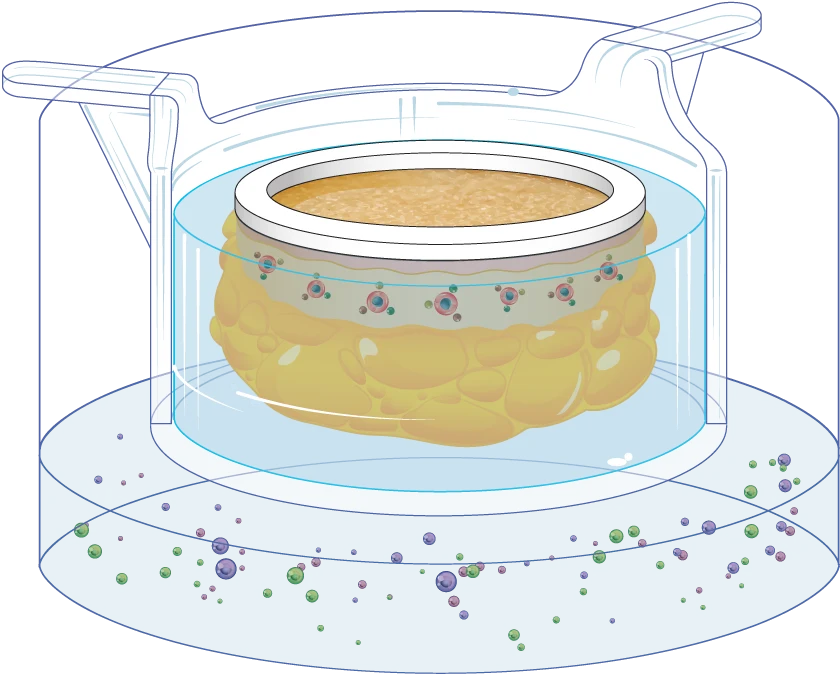
For the purpose of anti-psoriasis drug studies, the InflammaSkin® model’s resident T-cells are activated in situ by an IP-protected cocktail. The models are then cultured for up to 7 days with a chemically-defined culture medium supplemented with a pro-inflammatory cytokine cocktail to induce Th17/Th1 T-cell polarization.
Scientific validation of InflammaSkin®
Characterization of histological changes after induction of Th17/Th1 inflammation
Hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed on 5 µm-thickness skin cross-sections. The histological analysis of the InflammaSkin® model shows epidermal anomalies that are characteristic of psoriasis, in contrast to non-inflamed ex vivo skin models and the same model treated with the pro-inflammatory cocktail. All images are representative of the whole sample. Scale bar is 100 µm.
No induction
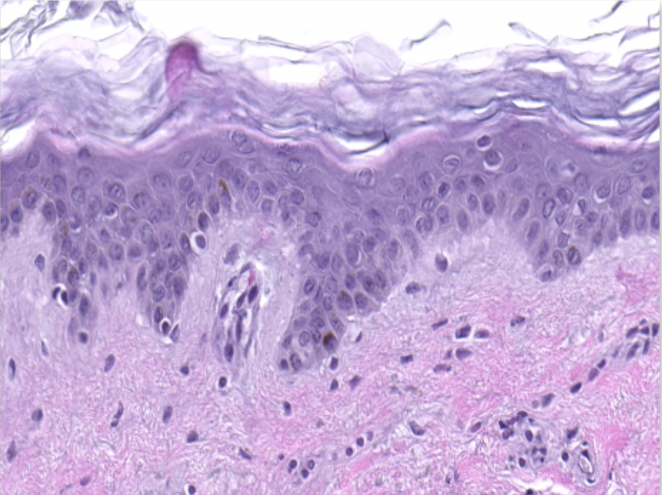
Healthy ex vivo human skin model cultured under basal conditions.
No T-cell activation
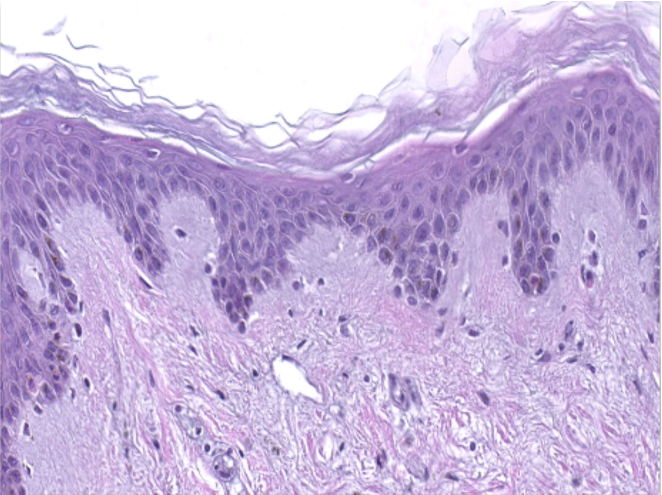
Skin model cultured in the presence of a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail but without T-Cell activation.
InflammaSkin®
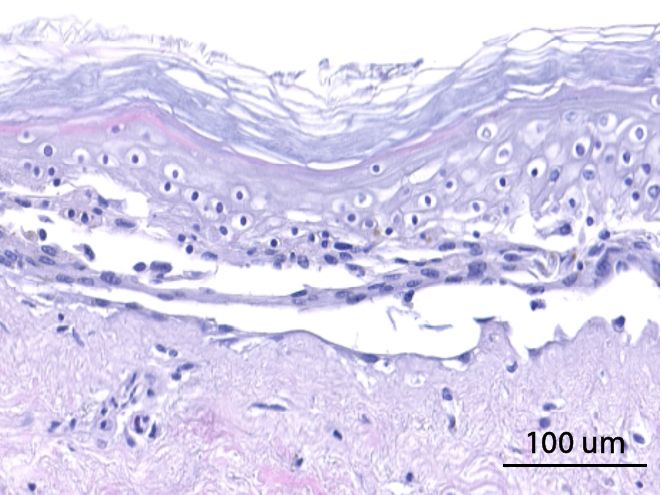
InflammaSkin® Model with T-Cell activation cocktail, cultured in the presence of a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail for 7 days.
Expression of pro-inflammatory markers in InflammaSkin®
Epidermal activation is shown by the over-expression of the psoriasis-associated pro-inflammatory markers Keratin 16 (K16) and psoriasin (S100A7). Anti-S100A7 and anti-K16 immunofluorescence staining procedures were performed on 5 µm-thickness skin cross-sections. Red and cyan signals indicate a positive signal and DAPI-counterstain nuclei respectively. The dotted white lines represent the epidermal-dermal junction. Epidermal and dermal compartments are located above and below the dotted line respectively. All images are representative of the whole sample. Scale bar is 100 µm.
No induction
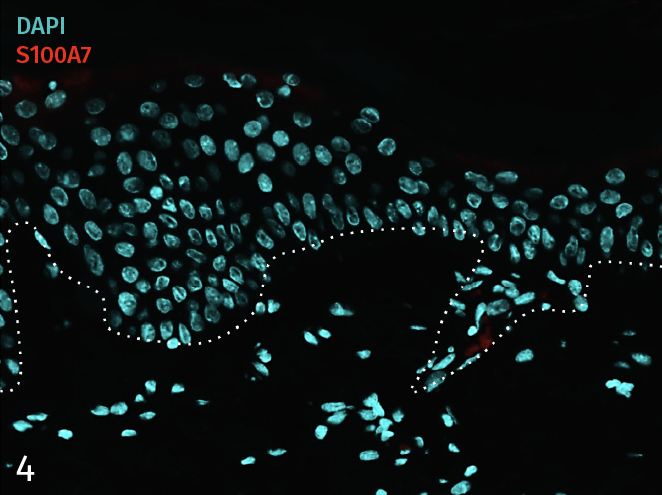
4 – Presence of pro-inflammatory marker Psoriasin (S100A7) in a healthy ex vivo skin model cultured under basal conditions.
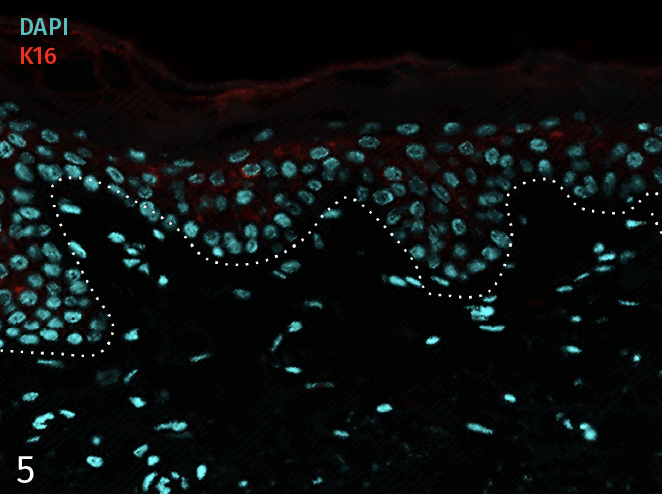
5 – Presence of pro-inflammatory marker Keratin 16 (K16) in a healthy ex vivo skin model cultured under basal conditions.
No T-cell activation
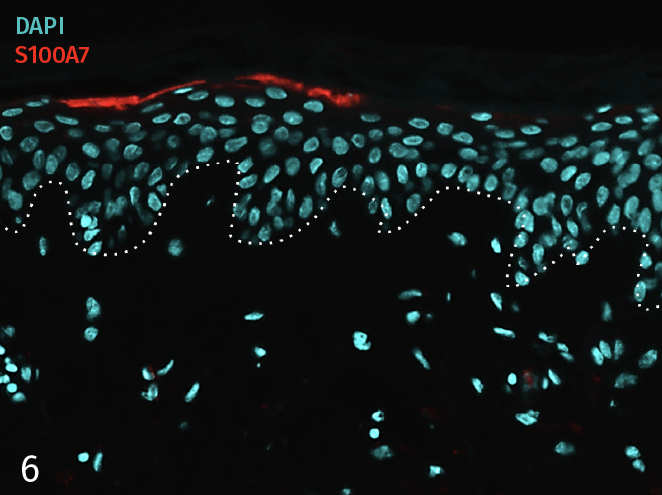
6 – Presence of pro-inflammatory marker Psoriasin (S100A7) in a skin model cultured in a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail but without T-Cell activation.
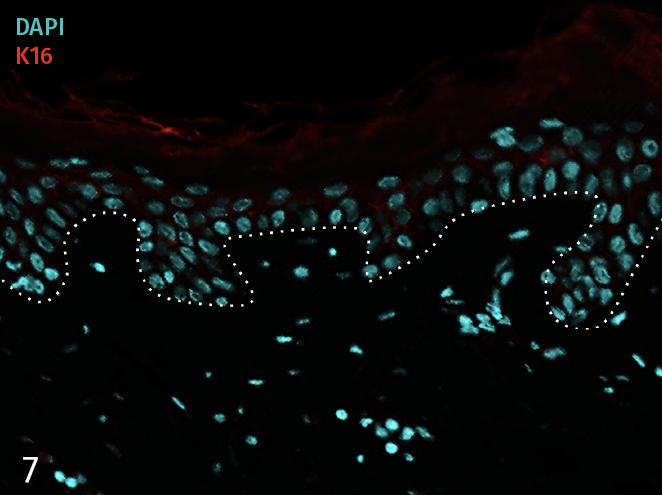
7 – Presence of pro-inflammatory marker Keratin 16 (K16) in a skin model cultured in a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail but without T-Cell activation.
InflammaSkin®
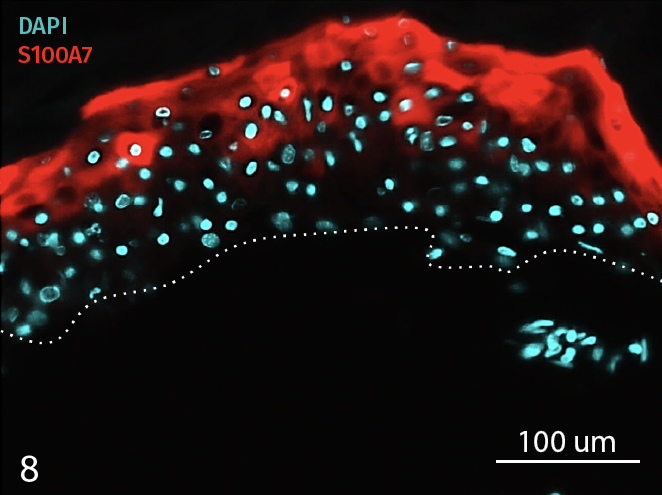
8 – Presence of Psoriasin (S100A7) in an InflammaSkin Model with T-Cell activation, cultured in a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail for 7 days.
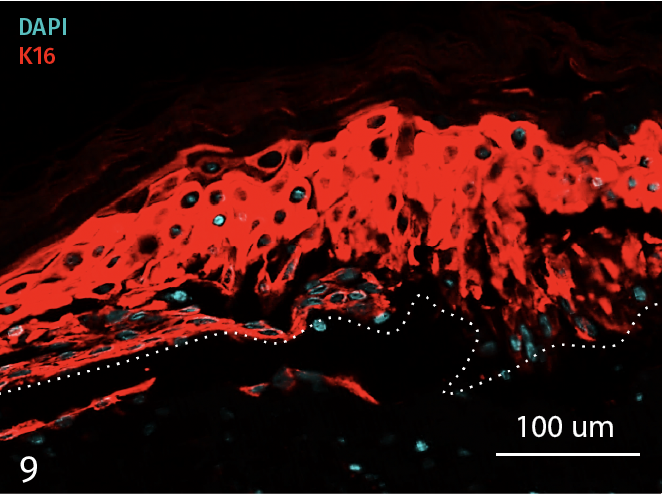
9 – Presence of Keratin 16 (K16) in an InflammaSkin Model with T-Cell activation, cultured in a Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail for 7 days.
Release of pro-inflammatory cytokines after 7 days of culture
The analysis of cytokine levels in culture media at day 7 shows sustained secretion of IL-17A and IL-22 (IFN-γ and TNF-α as well as the lack of IL-4 expression, data not shown) compared to non-inflamed ex vivo skin models, supporting successful activation and differentiation of Th17/Th1 cells.
The models were either cultured under basal conditions (no induction), in the presence of the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail (no T-Cell activation) and injected with activation cocktail and cultured in the presence of the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail (InflammaSkin®) for 7 days. Protein levels of IL-17A (A), IL-22 (B), INF-γ (C) were measured by ELISA (IL-22) and MSD in supernatant samples harvested after 7 days of culture. Lowest limit of detection (LLOD) is indicated by a dotted line for each cytokine. Data are expressed as mean value +/- SEM of pg/mL of secreted cytokines models obtained from 3 different donors. **P<.01
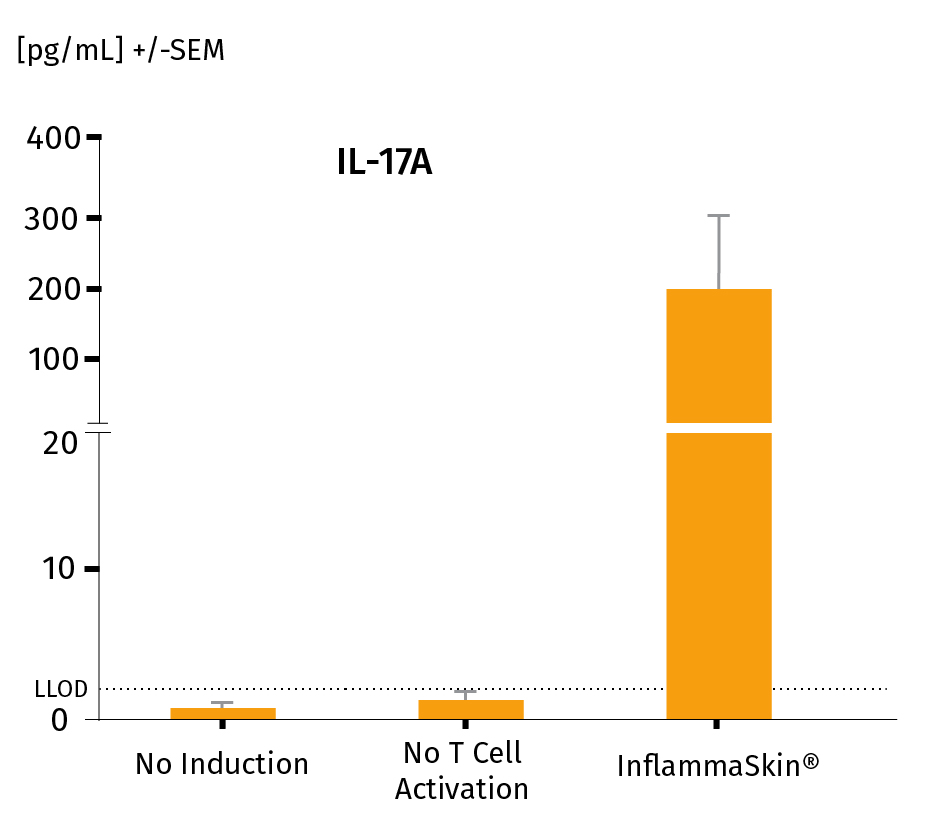
IL-17A protein levels in a healthy NativeSkin® model, a model cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail and the InflammaSkin® model with T-Cell activation cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail.
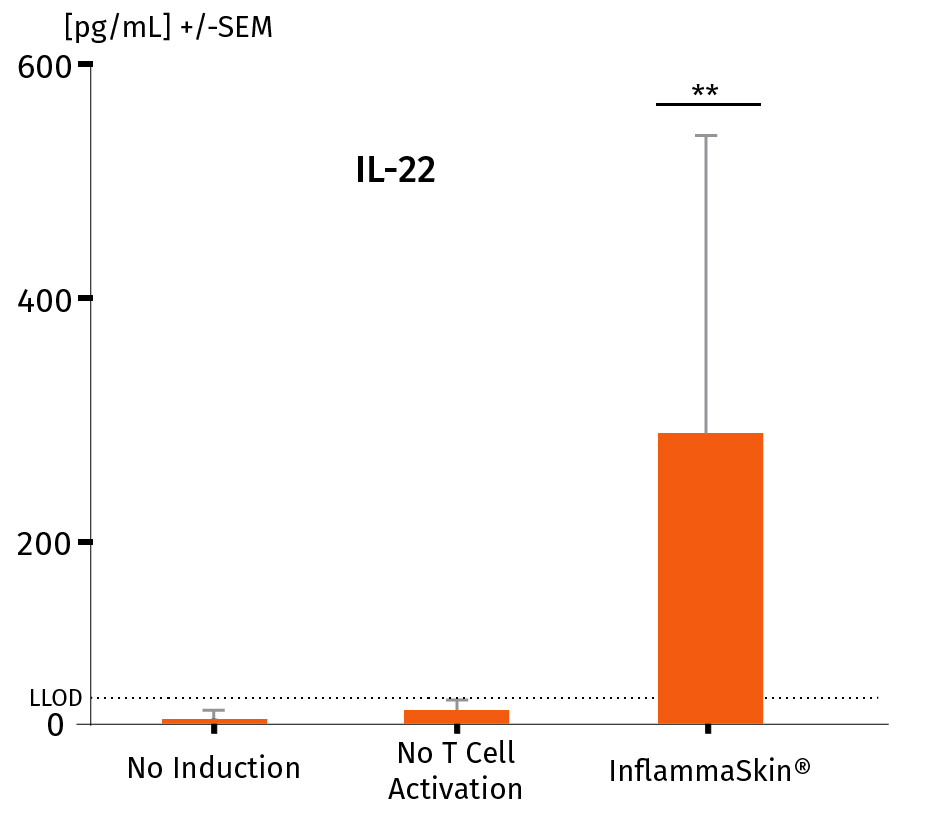
IL-22 protein levels in a healthy ex vivo skin model, a model cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail and the InflammaSkin® model with T-Cell activation cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail.
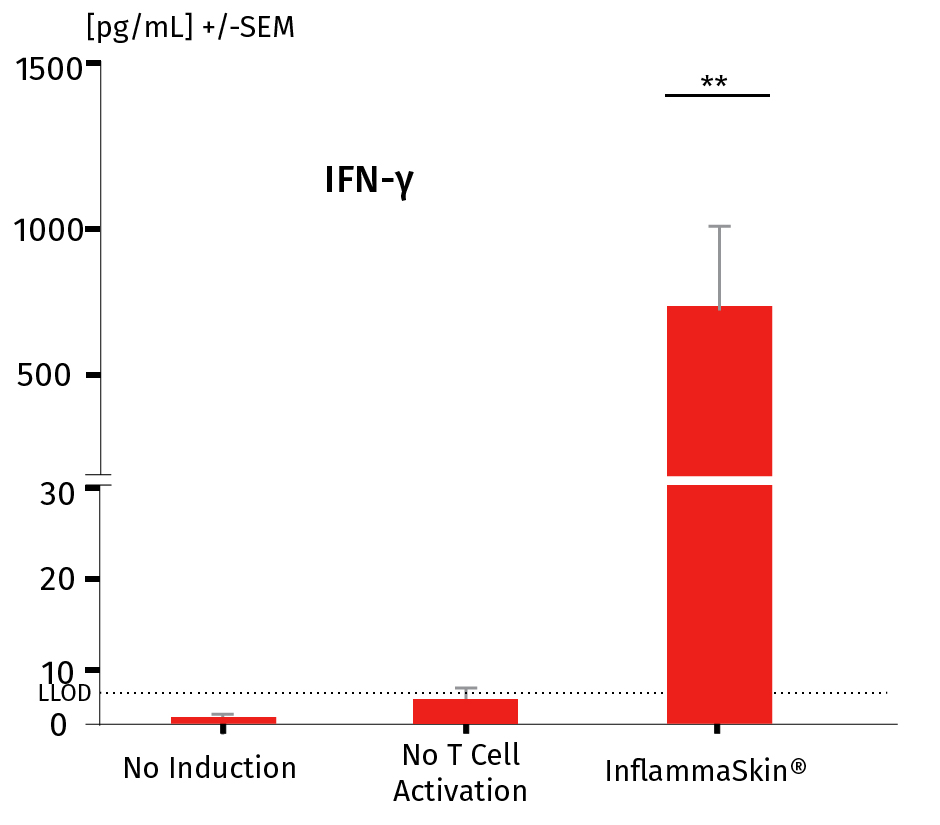
INF-γ protein levels in a healthy ex vivo skin model, a model cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail and the InflammaSkin® model with T-Cell activation cultured in the Th17/Th1 polarization cocktail.
Building on the robust validation data outlined in the previous section, the InflammaSkin® model empowers researchers to assess the efficacy of anti-inflammatory treatments with precision. This model is meticulously designed to evaluate therapies targeting key psoriasis pathways, including T cells and cytokines such as IL-17, IL-22, and TNF-α.
Whether you’re focusing on early intervention with prophylactic compounds (Day 0 administration) or addressing established inflammation with therapeutic treatments (Day 3 administration), InflammaSkin® adapts to your research needs.
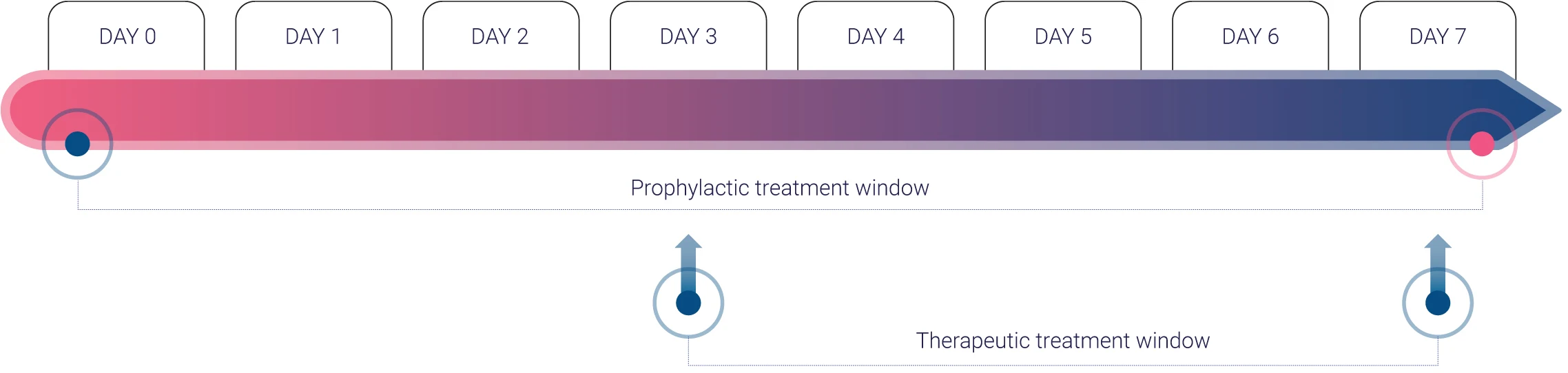
Flexible administration routes
- Topical applications for localized treatment effects
- Subcutaneous delivery for systemic exposure profiles
- Systemic route to explore broader pharmacodynamic effects
With its proven validity and versatile application options, InflammaSkin® is the ideal tool for accelerating the development of innovative anti-inflammatory therapies.
Resources

Enhanced T Cell proliferation and activation in InflammaSkin®: A flow cytometry perspective
- Enhanced T Cell proliferation and activation in InflammaSkin®: A flow cytometry perspective.
July 2024 - Press Release - Scinai Immunotherapeutics announces promising results in an in-vivo proof-of-concept psoriatic human skin model
- Scinai Immunotherapeutics Announces promising results in an in-vivo proof-of-concept psoriatic human skin model
- PR – July 15th, 2024
- “The results confirm and build upon previous reported results from ex-vivo studies done with human skin specimens (conducted by Genoskin) and in a plaque psoriasis in vitro model with human skin tissue grown in a dish.”
- PR – July 15th, 2024
June 2024 - Challenges in psoriasis research: A systematic review of preclinical models.
Published in Karger – June 10, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1159/000538993.
Ana Ubago-Rodríguez, María I. Quiñones-Vico, Manuel Sánchez-Díaz, Raquel Sanabria-de la Torre, Álvaro Sierra-Sánchez, Trinidad Montero-Vílchez, Ana Fernández-González, Salvador Arias-Santiago.
Dec 2023 - Press Release - Scinai announces promising results in a psoriatic human skin model
-
Scinai announces promising results in a psoriatic human skin model.
- PR – Dec 12th, 2023
- “The study, conducted by Genoskin, a pioneering French biotechnology company, aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of Scinai’s NanoAbs. Genoskin’s proprietary human skin models were induced for expression of plaque psoriasis symptoms to enable ex‑vivo examination of the therapeutic effects of drugs targeting underlying mechanisms in the pathogenesis of plaque psoriasis, particularly the IL-17 family of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This disease-induced skin model reproduces key features of plaque psoriasis tissue morphology as well as the cytokine profile associated with the inflammatory state of plaque psoriasis lesions. Genoskin’s model has been successfully validated as a reliable ex-vivo system for testing drugs aimed at plaque psoriasis.”
- PR – Dec 12th, 2023
December 2023 - The development of human ex vivo models of inflammatory skin conditions.
Published in National Library of Medicine – December 8, 2023. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec;24(24):17255. doi:10.3390/ijms242417255.
Eddy Hsi Chun Wang, Rebecca Barresi-Thornton, Li-Chi Chen, Maryanne Makredes Senna, I-Chien Liao, Ying Chen, Qian Zheng, Charbel Bouez
February 2021 - Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate foam inhibits Th17 cytokine secretion and improves epidermal barrier markers in a human Th17 skin inflammation model
- Calcipotriol/Betamethasone Dipropionate foam inhibits Th17 cytokine secretion and improves epidermal barrier markers in a human Th17 skin inflammation model.
- Published in Dermatologic Therapy – 2021 Feb;11(1):265-274
- Paola Lovato, Li Jiang, Josephine Hebsgaard, David A Ewald, Hanne Norsgaard
- Published in Dermatologic Therapy – 2021 Feb;11(1):265-274
October 2020 - Development and characterization of a human Th17 driven ex vivo skin inflammation model
- Development and characterization of a human Th17‐driven ex vivo skin inflammation model
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – Oct. 2020;29(10):993-1003.
- Claire Jardet, Anthony David, Emilie Braun, Pascal Descargues, Jean-Louis Grolleau, Josephine Hebsgaard, Hanne Norsgaard, Paola Lovato
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – Oct. 2020;29(10):993-1003.
January 2020 - Translational drug discovery and development with the use of tissue-relevant biomarkers: Towards more physiological relevance and better prediction of clinical efficacy
- Translational drug discovery and development with the use of tissue-relevant biomarkers: Towards more physiological relevance and better prediction of clinical efficacy
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – 2020 Jan;29(1):4-14
- Peter Florian, Klaus R Flechsenhar, Eckart Bartnik, Danping Ding-Pfennigdorff, Matthias Herrmann, Paul J Bryce, Frank O Nestle
- Published in Experimental Dermatology – 2020 Jan;29(1):4-14
October 2019 - Improvements of both inflammation and skin barrier in a human Th17 skin inflammation model by topical treatment with fixed-dose combination calcipotriene/betamethasone dipropionate foam
- Improvements of both inflammation and skin barrier in a human Th17 skin inflammation model by topical treatment with fixed-dose combination calcipotriene/betamethasone dipropionate foam
- Published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology – October 01, 2019, Volume 81, Issue 4, Supplement 1, AB79
- Hanne Norsgaard, Paola Lovato, Li Jiang, Josephine Hebsgaard, David Adrian Ewald
- Published in Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology – October 01, 2019, Volume 81, Issue 4, Supplement 1, AB79
September 2019 - Poster - Evaluation of pharmacological responses to subcutaneous injection of adalimumab in InflammaSkin®, a full-thickness human ex vivo skin model reproducing key features of psoriatic lesions
- Evaluation of pharmacological responses to subcutaneous injection of adalimumab in InflammaSkin®, a full-thickness human ex vivo skin model reproducing key features of psoriatic lesions
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
- C. Jardet (Genoskin), E. Bartnik (Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland), D. Ding-Pfennigdorff (Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland), E. Braun (Genoskin), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
September 2017 - Poster - Evaluation of pharmacological responses in a fully human ex vivo skin model following in situ T cell activation with Th17/Th1 psoriasis-like phenotype
- Evaluation of pharmacological responses in a fully human ex vivo skin model following in situ T cell activation with Th17/Th1 psoriasis-like phenotype damage and impairment of protein quality control systems in keratinocytes exposed to a volatile organic compounds cocktail
- Scientific Poster presented at the 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 27 to 30, 2017
- P. Lovato (LEO Pharma), C. Jardet (Genoskin), E. Pagès (Genoskin), H. Norsgaard (LEO Pharma), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 27 to 30, 2017